Author: CHEN Lixing
Schizophrenia, as defined by the NIH National Institute of Mental Health, is a “mental disorder characterized by disruptions in thought processes, perceptions, emotional responsiveness, and social interactions.” Symptoms of schizophrenia can be psychotic ones such as hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder, but also may include, reduced emotional expression, reduced motivation to accomplish goals, difficulty in social relationships, motor impairment, and cognitive impairment.
According to the statistics of the World Health Organization, about 20 million people worldwide are plagued by the disease【1】. The cause of schizophrenia is not yet clear. Recent studies have pointed out that genetics, environmental factors, brain chemical reactions and changes in brain structure may all induce schizophrenia. It is usually diagnosed sometime from the late teens to the early thirties, although the NIH states that it “tends to emerge earlier in males (late adolescence – early twenties) than females (early twenties – early thirties)”.
At present, the number of patients diagnosed with schizophrenia in China is increasing. According to the Lancet’s publication, the lifetime prevalence rate in China has reached 0.6% of the total population, while the urban population living with schizophrenia is significantly more than that in rural areas, with the former being 1.1% and the latter being only 0.1% 【2】. At the same time, due to social prejudices and incomplete understanding of the disease, only 8% of patients with mental disorders in China have ever sought professional help, and only 5% of patients have received professional diagnosis and treatment 【3】. Improving people’s awareness of mental illness and providing appropriate drugs to help patients control the disease have become the key to solving the burden of mental illness in China.
China and the US lead the antipsychotic drug market
The global market for antipsychotic drugs reached US$14.9 billion in 2018. With a compound annual growth rate of 4% it is expected to reach US$20 billion by 2026. Drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia account for about 45% of the total antipsychotic drugs. In 2018, the market size reached US$6.7 billion and is expected to reach US$9.2 billion by 2026【4】.
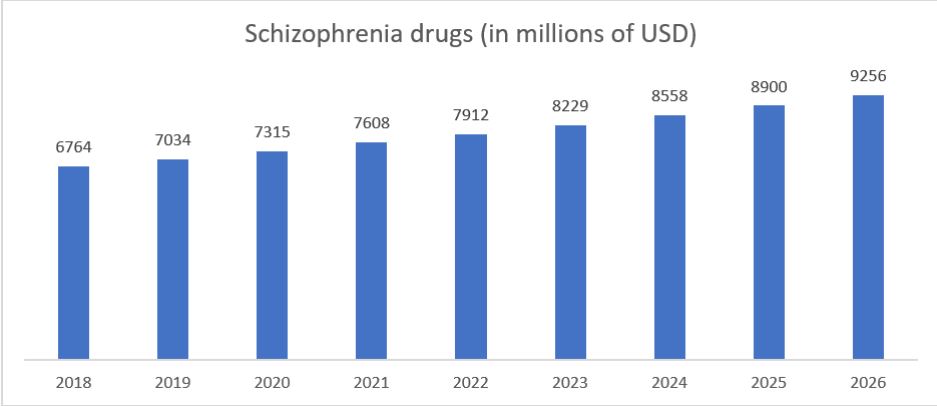
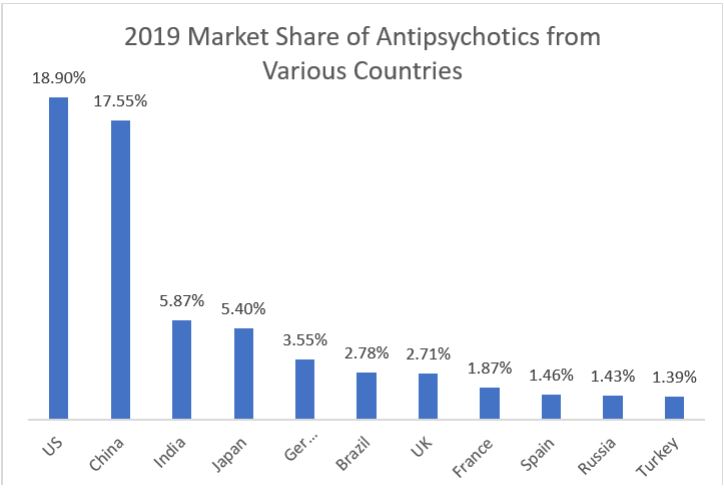
Another report pointed out that the United States is currently the largest market for antipsychotic drugs, accounting for 18.9% of the world market share. The three Asian countries of China, India and Japan follow closely behind. The Icon Group survey report pointed out that Asia will occupy about 37% of the market share of antipsychotic drugs in the future. Those countries, led by China, are expected to become the largest market for such drugs【5】.
Prescribing the correct medicine can be challenging
Because schizophrenia does not have a clear pathogenesis and well-identified drug targets, the drugs currently used to treat it include a wide range of antipsychotic drugs. These drugs are used to treat depression, bipolar disorder, and other mental disorders in addition to treating schizophrenia.
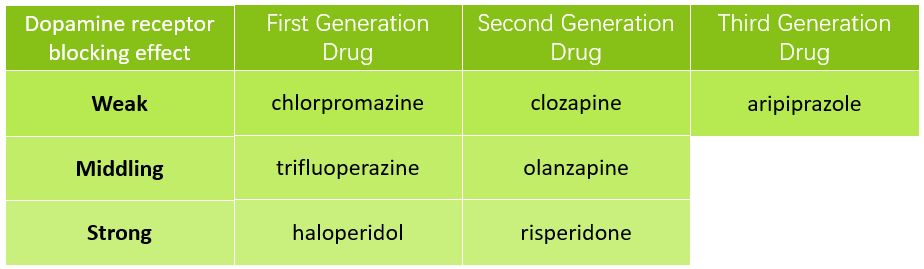
Antipsychotic drugs are divided into three categories. The first-generation antipsychotic drugs, also known as typical antipsychotic drugs, are mostly dopamine antagonists. The second-generation antipsychotic drugs, also known as atypical antipsychotics, block dopamine receptors as well as serotonin (5-HT) receptors. Compared with the first-generation drugs, they have the advantages of more significant therapeutic effects and fewer adverse reactions.
At present, the FDA has only approved one third-generation antipsychotic drug, aripiprazole, to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Its mechanism is a partial agonist of dopamine receptors and serotonin receptors. The current treatment of schizophrenia is based on second- and third-generation antipsychotic drugs. However, drugs are not effective for about 30% of patients with schizophrenia【6】 and new treatment methods and drugs are urgently needed.
Pharmaceutical companies that conducted original research lose their advantage
At present, the mainstream drugs to treat schizophrenia are second-generation and third-generation antipsychotics, of which second-generation drugs account for 74.2% of the total market share. Eli Lilly’s Zyprexa has reached annual sales of US$4 billion, and AstraZeneca’s Seroquel has reached US$5.8 billion annual sales.
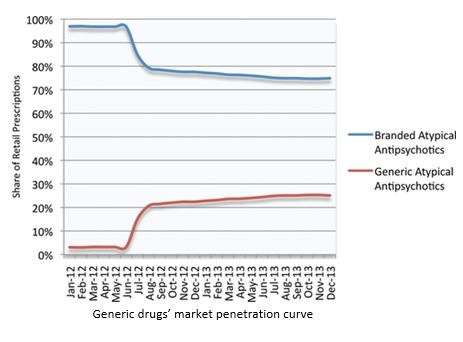
However, the time to market for second-generation drugs was mostly in the 1970s, and most of them have lost patent protection. The market penetration rate of generic drugs will reach 25% within six months of the drug going to market【7】, and the price of the generics is about 3% of the original drug. Such low prices and equivalent effects result in the original drug losing its competitive advantage.
For example, the generic drugs produced by Prasco Laboratories and Teva Pharmaceuticals caused Eli Lilly’s Zyprexa sales to drop by 68%. Meanwhile, generic drugs received a total of US$980 million in sales. Seroquel’s sales today are consequently only about $100 million. Under the pressure of operating distribution, AstraZeneca has transferred the sales rights of the United States and Canada to Cheplapharm in Germany.
Researching and developing new drugs is full of difficulties
At present, research and development of schizophrenia treatments is difficult due to high costs and generally unsatisfactory effects. Since 2008, the number of related clinical studies has been steadily decreasing.
In addition, there is frequent news of the failure of clinical studies of schizophrenia treatments, such as Acadia’s Nuplazid, which is used to treat hallucinations and delusions related to Parkinson’s. It went through phase III clinical trials to treat schizophrenia. While it demonstrated a certain effect, it still could not reach the primary endpoint and there was no significant difference compared with the control group. In addition, Lundbeck’s Lu AF35700 and Minerva’s Min-101 have frequently encountered back luck, experiencing experiment failures in phase III clinical trials.
The type I glycine transporter (GlyT1) inhibitor bitopertin was once considered to be the add-on therapy for the recessive symptoms of schizophrenia with the most potential; however, in phase III clinical trials, Waterloo was confirmed to be no different from the placebo control group.
Attempts on other targets such as PDE10 and mGlu2/3 have not significantly improved the symptoms of schizophrenia. Although there are still pharmaceutical companies trying to capture these targets and provide more options for the treatment of schizophrenia, numerous failures have cast a haze on drug development.
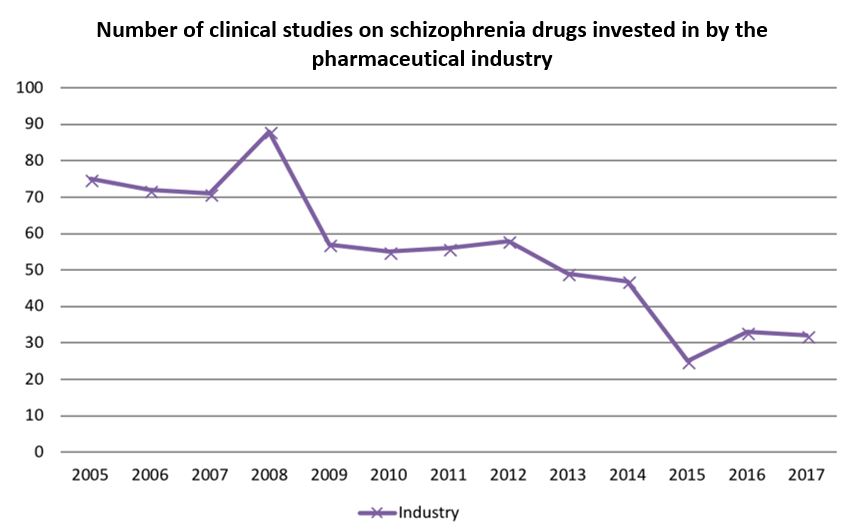
With the rise of emerging powers, traditional manufacturers are facing challenges
Many traditional multinational pharmaceutical companies, such as Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca, have not recently conducted drug research on new schizophrenia treatments. Currently, the main research forces such as Lundbeck, Alkermes, Otsuka and other pharmaceutical companies are mainly improving on the basis of existing drugs. Meanwhile, small companies like Bioxcel, Karuna, and Intra-Cellura therapy are more focused on the development of new drugs which try to treat schizophrenia by targeting different mechanisms and targets.
Domestic Chinese pharmaceutical companies seem to be still stuck in the quagmire of the competition of second-generation antipsychotic drugs, and they have few plans for internal research and development of innovative drugs.
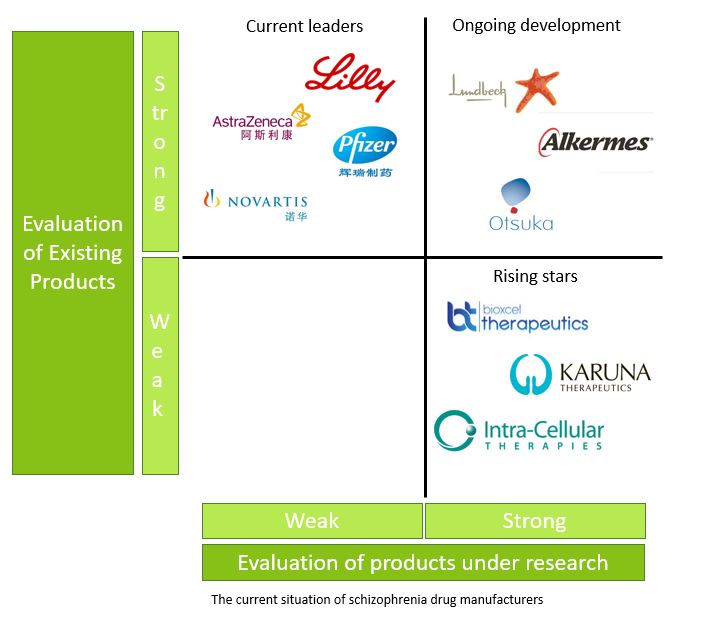
Antipsychotics have much room for improvement
The current mainstream second-generation and third-generation antipsychotic drugs still have many shortcomings. Because of their strong generality, they are not ideal for treating a specific disorder. Finding the most effective drugs for the patient is often done by trial and error, which is time-consuming and costly. At the same time, prejudices generated by the social environment makes it more difficult for patients to seek medical advice for mental health.
Numerous adverse reactions【8】: Almost all second-generation antipsychotic drugs have a strong sedative effect, which may affect the patient’s normal daily life and work. In addition, it may cause weight gain, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and adverse gastrointestinal reactions. Various adverse reactions greatly affect the patient’s medication compliance.
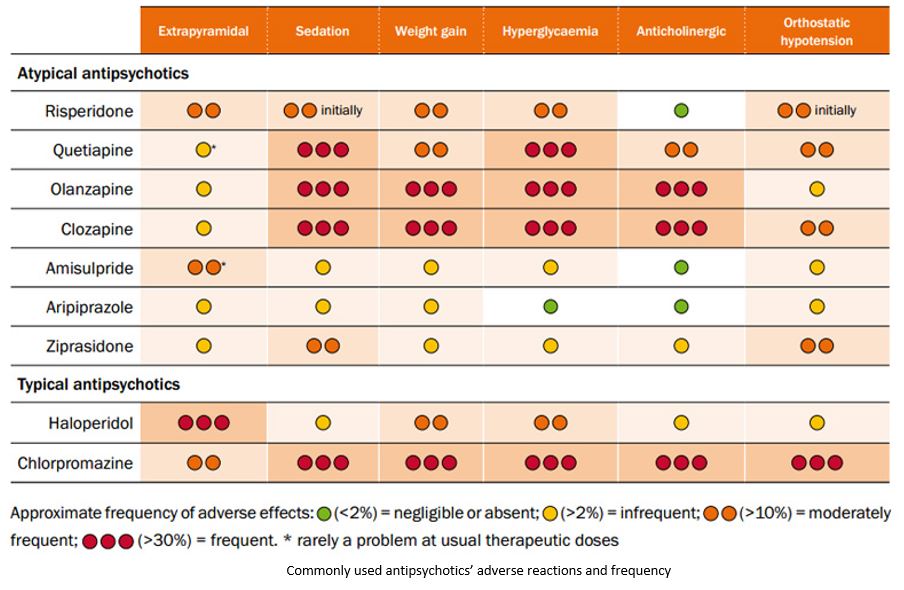
Refractory schizophrenia【9】: According to statistics, 30% of patients with schizophrenia do not respond to today’s antipsychotic treatment. The medical community calls it refractory schizophrenia. Currently only clozapine has a certain effect on it. However, clozapine itself causes a variety of adverse reactions. It is difficult for doctors to assess whether the benefits of clozapine outweigh the disadvantages during administration. Although genetic diagnosis can help predict the effect of treatment, a dedicated drug may better solve this problem.
High recurrence rate【10】: The recurrence rate of patients with schizophrenia after stopping the drug is 52%, which is 36% higher than that of people who continue to use the drug for maintenance treatment. The average recurrence interval is about 6 months. Current drug treatment seems to require life-long medication for patients to minimize the possibility of recurrence, which brings a lot of economic burden to patients.
Drug misuse and serious abuse【11】: According to estimates by the US human rights regulatory agency, nursing homes in the US prescribe antipsychotic drugs to as many as 179,000 elderly people every week without diagnosis, thereby achieving a sedative effect and reducing problems for management. On the other hand, due to the sedative and anti-anxiety effects of antipsychotic drugs, some people gradually become addicted after taking the drugs, which can result in drug abuse. Recently, the FDA has raised concerns about drug addiction to Alkermes Pharmaceuticals’ ALKS 3831 drug.
Development trends
Break down the symptoms and prescribe the right medicine: The current symptoms of schizophrenia are divided into dominant (hallucinations, delusions, confusion of thinking and speech), recessive (low mood, poor speech and thought, apathy), cognitive dysfunction, depression, mania, and others. As the level of diagnosis of schizophrenia still needs to be improved, patients with recessive symptoms may find it difficult to obtain medication without actively seeking medical treatment. At the same time, current antipsychotic drugs are mainly aimed at overt symptoms. Currently, drugs developed by companies such as Karuna Therapeutics and CoNCERT Pharmaceuticals have curative effects on both dominant and recessive symptoms.
Long-acting and low-toxic drugs are needed now: current antipsychotic drugs have relatively high-frequency side effects, and basically need to be taken every day. When patients experience side effects, their compliance with medications can be greatly reduced, which will affect the treatment of diseases and waste time and money. Studies have shown that the non-compliance rate of non-long-acting drugs for schizophrenia is about 50%, while the compliance rate of long-acting drugs can reach 96%【12】. Therefore, long-acting modified drugs could reduce the rate of non-compliance, and drugs with low toxicity could allow patients to experience less pain. Currently Braeburn and Intra-Cellular Therapies are working hard in this direction.
Multi-dimensional treatment, both rigid and flexible: The use of medication is only part of the treatment of schizophrenia. Other long-term assistance could include physical therapy (deep brain stimulation), behavior therapy, cognitive training for hidden symptoms, psychological counseling and social reintegration training to better help patients face the disease and actively treat it. At the same time, we should also make a conscious effort to put aside any biases for patients with mental health disorders, accept and treat them, and help them better integrate into society and work.
Create a precedent
Although the development of schizophrenia drugs is difficult, some small pharmaceutical companies are able to break through existing thinking. They can break away from the limitations of current targets, subdivide the symptoms of psychiatric disorders and conduct in-depth research. It is this spirit that has allowed some small companies to stand out and pioneer anti-schizophrenia drugs.
New opportunities brought by new targets

Newron Pharmaceuticals’ drug NW-3509A is a selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker for the adjuvant treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Its phase II clinical trials demonstrated its antipsychotic efficacy as an additional treatment of risperidone or aripiprazole, and it is more effective in young people. At present, the drug has completed phase II clinical trials and the FDA will consider whether to approve III clinical trials after Newron completes additional studies. Although the drug was once plagued by safety issues, if it can successfully enter phase III clinical trials, it could become a boon for young patients.

The xanomeline and trospium chloride compound formulation pioneered by Karuna Therapeutics targets the muscarinic receptor. Since xanomeline exerts a therapeutic effect and can cause serious adverse reactions, trospium chloride is added to neutralize it. KarXT is used to treat schizophrenia. Its phase II clinical trials have demonstrated its excellent safety and effective improvement of the overt and recessive symptoms of schizophrenia. Currently, the drug is planned to enter phase III clinical trials by the end of 2020. The drug is the first compound drug used to treat schizophrenia. It uses the mechanism of action between the drugs to complement each other. Karuna Therapeutics’ stock price soared by 134% when the phase II clinical trial data was released.

CoNCERT Pharmaceuticals’ CTP-692 is a deuterated form of D-serine that acts as an NMDA receptor agonist. It has been found in clinical research that it has a certain effect on the dominant and recessive symptoms of schizophrenia and the improvement of cognitive function. It is currently in phase II clinical trials as a co-treatment.

Taiwanese company SyneuRx’s Naben is a D-amino acid oxidase inhibitor that enhances the function of glutamine-NMDA receptors by inhibiting the decomposition of D-serine. Current research has found that it can improve both the dominant and recessive symptoms of schizophrenia. At present, it has entered phase II/III clinical trials. NMDA receptor is a popular target related to psychiatric treatment in recent years. Schizophrenia, depression, and other mental disorders are all related to it. No matter who can seize the opportunity, it is likely to get a lot of returns in the field of psychiatric treatment.
Long-acting improved drugs become more popular

Braeburn is currently working on a six-month long-acting implant of risperidone to treat schizophrenia. Risperidone is a dopaminergic D2 receptor and serotonin receptor inhibitor. It is used to treat opioid use disorder and schizophrenia. Its use to treat opioid use disorder has received tentative approval from the FDA. The phase III clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia has also been completed. The drug will likely be the first long-acting six-month schizophrenia drug, which could effectively improve the patient’s medication compliance and better treat patients.

Intra-Cellular’s Caplyta has been approved by the FDA and will be launched in early 2020. Its mechanism of action is similar to but different from the second-generation antipsychotic drugs. It has fewer adverse reactions and has higher safety as an antipsychotic drug.
In addition, the ITI-007 platform that Intra-Cellular is studying uses lumateperone as the initial treatment, plus a long-acting injection. Lumateperone is a serotonin receptor antagonist and dopamine receptor antagonist and is used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar depression. Its first phase III clinical trial reached the primary clinical endpoint, showing its antipsychotic efficacy and excellent safety.

Bioxcel’s BXCL501 is a sublingual membrane of dexmedetomidine used to treat agitation in patients with schizophrenia. The sublingual membrane has the advantages of rapid onset of action and simple administration. At the same time, it does not affect the patient’s cognition while providing a certain degree of sedation. At present, phase III clinical trials have been completed and its primary and secondary clinical endpoints have been reached, demonstrating a powerful therapeutic effect. Since dexmedetomidine itself is a commonly used anesthetic, it is difficult to control the dose due to the strong effect and there are possible side effects due to this excessive sedative effect. Some analysts said that if the drug can be approved, it is expected to become the next billion-dollar blockbuster drug.
Summary
In many cases of those who suffer from schizophrenia, patients may not realize that they have the disease. However, increasingly serious symptoms may affect the patients’ daily lives and the people around them. Although the disease is gaining more and more attention, the extremely low rate of clinical visits indicates that in addition to insufficient mental health education, there’s an implication of a huge potential market. With the emergence of new, dedicated antipsychotic drugs and the improvement of traditional drugs, we believe that in the near future, more mental patients will receive appropriate treatment and enter a brighter future.
About the author
CHEN Lixing is an investment analyst at MyBioGate with double master’s degree from KGI Graduate School and Drucker School of Management. As a graduate consultant, he provided strategic consulting services for Samumed and SomaLogic.
References
【1】https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia
【2】Huang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Z., Yu, X., Yan, J., …Wu, Y. (2019). Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. The Lancet Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(18)30511-x
【3】Phillips MR, Zhang J, Shi Q, et al. Prevalence, treatment, and associated disability of mental disorders infour provinces in China during 2001-05: an epidemiological survey[J]. Lancet,2009,373(9680):2041-2053.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60660-7.
【4】https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/antipsychotic-drugs-market-101390
【5】The 2019-2024 world outlook for Mental Disorder Drugs.
【6】https://www.nature.com/articles/s41537-019-0090-z
【7】https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ccl.idm.oclc.org/pmc/articles/PMC2861526/
【8】https://www.grepmed.com/images/3725/antipsychotics-pharmacology-sideeffects-decisionaid-psychiatry-comparison-atypical
【9】https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ccl.idm.oclc.org/pmc/articles/PMC5106233/
【10】https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ccl.idm.oclc.org/pmc/articles/PMC3599855/
【11】https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20180424.962541/full/
【12】https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ccl.idm.oclc.org/pmc/articles/PMC3782179/

0 Comments